As an actuator, stepper motor is one of the key products of mechatronics, which is widely used in various automation control systems. With the development of microelectronics and computer technology, the demand for stepper motors is increasing day by day, and they are used in various national economic fields.
01 What is a stepper motor
Stepper motor is an electromechanical device that directly converts electrical pulses into mechanical motion. By controlling the sequence, frequency and number of electrical pulses applied to the motor coil, the stepper motor's steering, speed and rotation angle can be controlled. Without the use of a closed-loop feedback control system with position sensing, precise position and speed control can be achieved using a simple, low-cost open-loop control system composed of a stepper motor and its accompanying driver.
02 stepper motor basic structure and working principle
Basic structure:
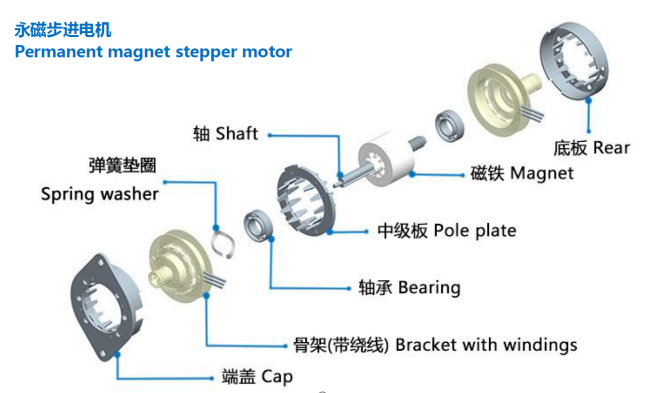
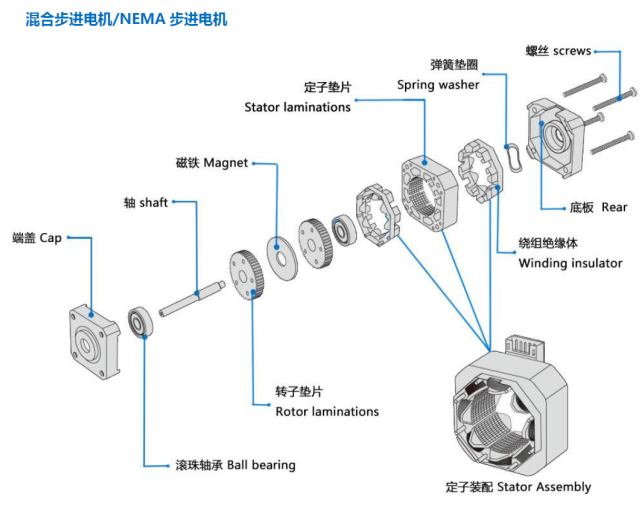
Working principle: stepper motor driver according to the external control pulse and direction signal, through its internal logic circuit, control the stepper motor windings in a certain timing sequence forward or reverse energized, so that the motor forward / reverse rotation, or lock.
Take 1.8 degree two-phase stepper motor as an example: when both windings are energized and excited, the motor output shaft will be stationary and locked in position. The maximum torque that will keep the motor locked at the rated current is the holding torque. If the current in one of the windings is redirected, the motor will rotate one step (1.8 degrees) in a given direction.
Similarly, if the current in the other winding changes direction, the motor will rotate one step (1.8 degrees) in the opposite direction of the former. When the currents through the coil windings are sequentially redirected to excitation, the motor will rotate in a continuous step in the given direction with very high accuracy. For 1.8 degrees of two-phase stepper motor rotation of a week takes 200 steps.
Two-phase stepper motors have two types of windings: bipolar and unipolar. Bipolar motors have only one winding coil per phase, the motor continuous rotation of the current in the same coil to be sequentially variable excitation, the design of the drive circuit requires eight electronic switches for sequential switching.
Unipolar motors have two winding coils of opposite polarity on each phase, and the motor
rotates continuously by alternately energizing the two winding coils on the same phase.
The drive circuit is designed to require only four electronic switches. In the bipolar
drive mode, the output torque of the motor is increased by about 40% compared to the
unipolar drive mode because the winding coils of each phase are 100% excited.
03, Stepper motor load
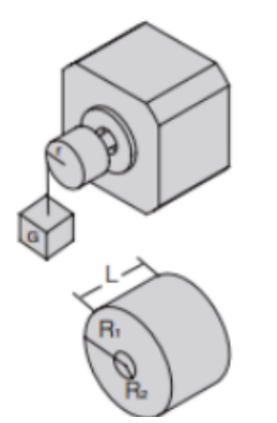
A. Moment load (Tf)
Tf = G * r
G: Load weight
r: radius
B. Inertia load (TJ)
TJ = J * dw/dt
J = M * (R12+R22) / 2 (Kg * cm)
M: Load mass
R1: Radius of outer ring
R2: Radius of the inner ring
dω/dt: Angular acceleration
04, stepper motor speed-torque curve
The speed-torque curve is an important expression of the output characteristics of stepper
motors.
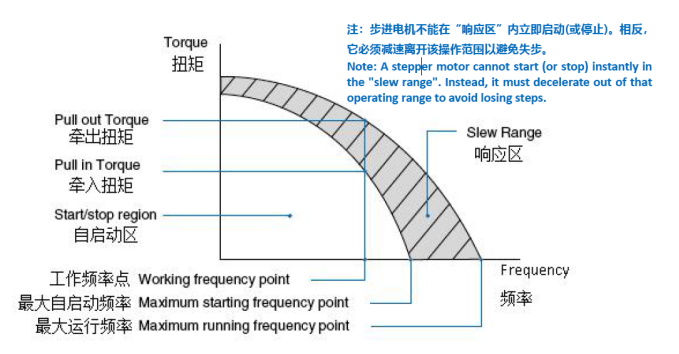
A. Stepper motor operating frequency point
The speed value of the stepper motor motor at a certain point.
n = q * Hz / (360 * D)
n: rev/sec
Hz: Frequency value
D: Drive circuit interpolation value
q: stepper motor step angle
For example, a stepper motor with a pitch angle of 1.8°, with a 1/2 interpolation drive (i.e., 0.9° per step), has a speed of 1.25 r/s at an operating frequency of 500 Hz.
B. Stepper motor self-start area
The area where the stepper motor can be started and stopped directly.
C. Continuous operation area
In this area, the stepper motor cannot be started or stopped directly. Stepper motors in this area must first pass through the self-start area and then be accelerated to reach the operating area. Similarly, the stepper motor in this area can not be directly braked, otherwise it is easy to cause the stepper motor out of step, must first be decelerated to the self-starting area and then braked.
D. Stepper motor maximum starting frequency
Motor no-load state, to ensure that the stepper motor does not lose step operation of the maximum pulse frequency.
E. Stepper motor maximum operating frequency
The maximum pulse frequency at which the motor is excited to run without losing a step under no load.
F. Stepper motor starting torque / pull-in torque
To meet the stepper motor in a certain pulse frequency to start and start running, without losing steps of the maximum load torque.
G. Stepper motor running torque/draw-in torque
The maximum load torque that satisfies the stable operation of the stepper motor at a certain pulse frequency without loss of step.
05 Stepper motor acceleration/deceleration motion control
When the stepper motor operating frequency point in the speed-torque curve of continuous operation region, how to shorten the motor start or stop acceleration or deceleration time, so that the motor runs longer in the best speed state, thereby increasing the effective running time of the motor is very critical.
As shown in the figure below, the dynamic torque characteristic curve of stepper motor is a horizontal straight line at low speed; at high speed, the curve decreases exponentially due to the influence of inductance.
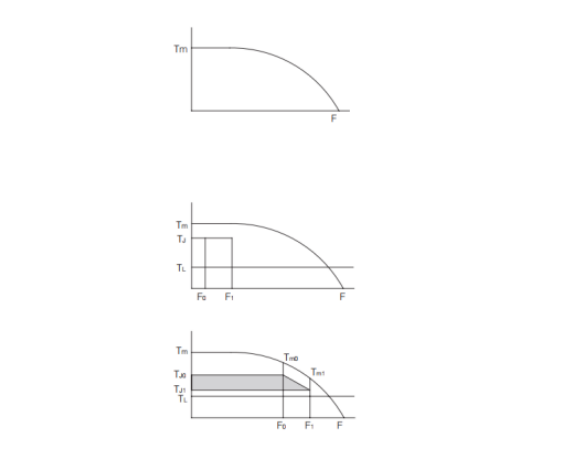
We know that the stepper motor load is TL, suppose we want to accelerate from F0 to F1 in the shortest time (t r), how to calculate the shortest time t r ?
(1) Normally, TJ = 70% Tm
(2) tr = 1.8 * 10 -5 * J * q * (F1-F0)/(TJ -TL)
(3) F (t) = (F1-F0) * t/tr + F0, 0<t<tr
B. Exponential acceleration in high speed condition
(1) Normally
TJ0 = 70%Tm0
TJ1 = 70%Tm1
TL = 60%Tm1
(2)
tr = F4 * In [(TJ 0-TL)/(TJ 1-TL)]
(3)
F (t) = F2 * [1 - e^(-t/F4)] + F0, 0<t<tr
F2 = (TL-TJ 0) * (F1-F0)/TJ 1-TJ 0)
F4 = 1.8 * 10-5 * J * q * F2/(TJ 0-TL)
Notes.
J indicates the rotational inertia of the motor rotor under load.
q is the rotation angle of each step, which is the step angle of the stepper motor in the
case of the whole drive.
In the deceleration operation, just reverse the above acceleration pulse frequency can be
calculated.
06 stepper motor vibration and noise
Generally speaking, stepper motor in no-load operation, when the motor operating frequency is close to or equal to the motor rotor's inherent frequency will resonate, serious will occur out of step phenomenon.
Several solutions for resonance:
A. Avoid the vibration zone: so that the motor's operating frequency does not fall within the vibration range
B. Adopt subdivision drive mode: Use micro-step drive mode to reduce vibration by
subdividing the original one step into multiple steps to increase the resolution of each
motor step. This can be achieved by adjusting the phase to current ratio of the motor.
Microstepping does not increase the step angle accuracy, but makes the motor run more
smoothly and with less noise. The torque is generally 15% lower for half-step operation
than for full-step operation, and 30% lower for sine wave current control.
Post time: Nov-09-2022
