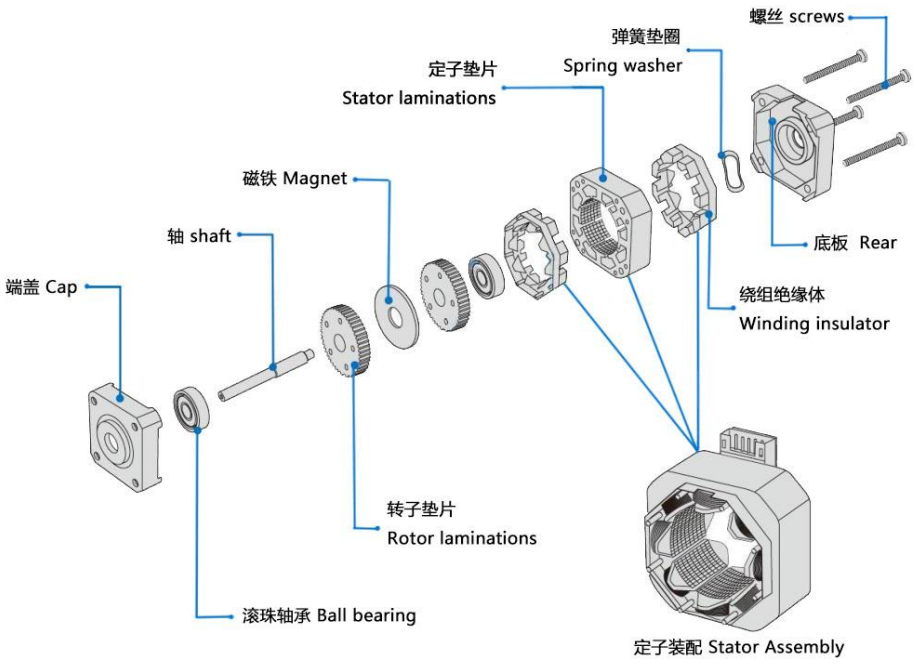
A stepper motor is an electric motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, and its output torque and speed can be precisely controlled by controlling the power supply.
I, the advantages of stepper motor

High precision
The angle of rotation of the stepper motor is proportional to the number of input pulses, so it is possible to precisely control the number and frequency of pulses to achieve accurate control of the motor position and speed. This characteristic makes stepper motors excel in applications that require high-precision positioning, such as CNC machine tools, printing presses, and textile machines.
Stepper motors usually have an accuracy of between 3% and 5% per step and do not accumulate the error from the previous step to the next, i.e. they do not generate cumulative errors. This means that stepper motors are able to maintain high positional accuracy and motion repeatability over long periods of time or continuous motion.
Highly controllable

Stepper motor operation is achieved by controlling the pulse current, so control of the motor can be realized through software programming. This programmability allows stepper motors to meet the needs of a wide variety of applications, such as automated production lines, robotics, and other fields.
Since the response of the stepper motor is only determined by the input pulse, open-loop control can be used, which makes the structure of the motor simpler and less expensive to control. Open-loop control also reduces system complexity and maintenance costs.
High torque at low speeds
Stepper motors have high torque output at low speeds, which makes them excellent in applications that require low speed and high torque, such as automatic labeling machines and packaging machines.
Stepper motors have maximum torque when stopped, a feature that makes them advantageous in applications where positional stability or resistance to external loads is required.
High reliability

Stepper motors have no brushes, thus reducing malfunctions and noise due to brush wear. This makes stepper motors highly reliable, with the life of the motor largely dependent on the life of the bearings.
Stepper motors have a simple structure, consisting of three parts: the motor itself, the driver and the controller, making installation and maintenance relatively easy.
Wide speed range

Stepper motors have a relatively fast speed range, and the speed of the motor can be changed by adjusting the pulse frequency. This allows the stepper motor to adapt to different working speeds and load requirements.
Good Start-Stop and Reverse Response
Stepper motors respond quickly to control signals when starting and stopping, and maintain high precision and stability when reversing. This feature makes the stepper motor in the need for frequent start-stop and reversal of the application has an advantage.
II, the disadvantages of stepper motors
Easy to lose step or overstep
If not properly controlled, stepper motors are susceptible to out-of-step or over-step. Out-of-step means that the motor fails to rotate in accordance with a predetermined number of steps, while out-of-step means that the motor rotates more than a predetermined number of steps. Both of these phenomena result in a loss of positional accuracy of the motor and affect the performance of the system.
The generation of out-of-step and over-step is related to factors such as the motor's load, rotational speed, and the frequency and amplitude of the control signal. Therefore, when using stepper motors, these factors need to be carefully considered and appropriate measures taken to avoid the occurrence of out-of-step and over-step.
Difficulty in reaching high rotational speeds
The rotational speed of a stepper motor is limited by its operating principle, and it is usually difficult to achieve a high rotational speed. Although it is possible to increase the speed of the motor by increasing the frequency of the control signal, too high a frequency will lead to problems such as motor heating, increased noise and may even damage the motor.
Therefore, when using stepper motors, it is necessary to select the appropriate speed range according to the application requirements and avoid running at high speeds for long periods of time
Sensitive to load changes
Stepping motors require real-time control of the number and frequency of current pulses during operation to ensure precise control of position and speed. However, in the case of large load changes, the control current pulse will be disturbed, resulting in unstable movement and even uncontrolled stepping.
To solve this problem, a closed-loop control system can be used to monitor the position and speed of the motor and adjust the control signal according to the actual situation. However, this will increase the complexity and cost of the system.
Low efficiency
Since stepper motors are controlled between constant stopping and starting, their efficiency is relatively low compared to other types of motors (e.g. DC motors, AC motors, etc.). This means that stepper motors consume more power for the same output power.
In order to improve the efficiency of stepper motors, measures such as optimizing control algorithms and reducing motor losses can be used. However, the implementation of these measures requires a certain level of technology and cost investment.
III, the scope of application of stepper motors:
Stepper motors are widely used in many fields because of their unique advantages and certain limitations. The following is a detailed discussion of the scope of application of stepper motors:
Robotics and automation systems

Stepper motors are widely used in industrial robots, automated production lines, and other fields. They can precisely control the motion speed and direction of robots and realize high-precision positioning and fast response in automated production processes.
CNC Machine Tools

Printers

Stepper motors are used to control the movement of the print head in devices such as inkjet and laser printers. By precisely controlling the movement of the motor, high-quality text and image printing can be realized. This feature makes stepper motors widely used in printing equipment.
Medical Devices
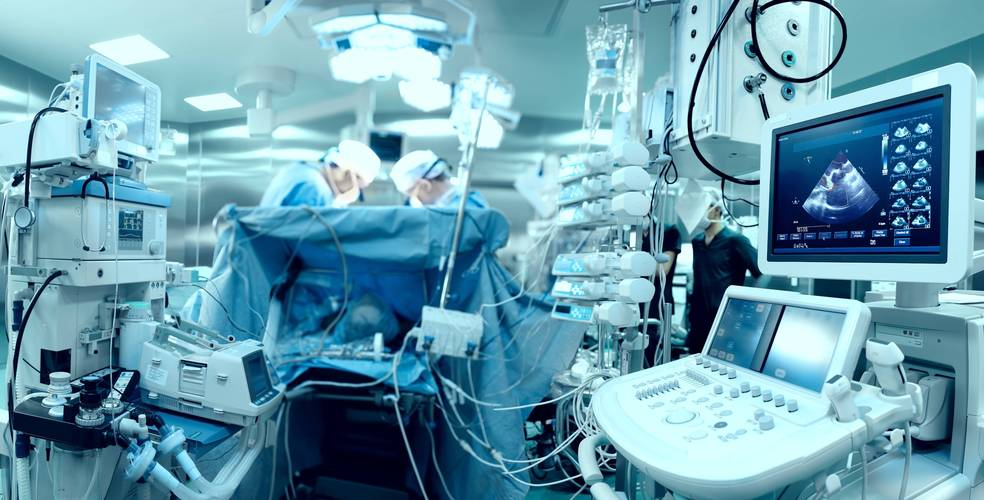
Stepper motors are used in medical imaging equipment (e.g. X-ray machines, CT scanners, etc.) to drive the movement of the scanning frame. By precisely controlling the movement of the motor, fast and accurate imaging of the patient can be realized. This feature makes stepper motors play an important role in medical equipment.
Aerospace

Stepper motors are used to control the motion of actuators in aerospace equipment such as satellite attitude control and rocket propulsion systems. Stepper motors exhibit good performance under the requirements of high precision and high stability. This characteristic makes stepper motors an important part of the aerospace field.
Entertainment and Gaming Equipment

Stepper motors are used to control the motion of actuators in devices such as laser engravers, 3D printers, and game controllers. In these devices, precise control of stepper motors is critical to achieving a high-quality product and a great user experience.
Education and Research

Stepper motors are used to control the movement of experimental platforms in scenarios such as laboratory instruments and teaching equipment. In education, the low cost and high accuracy of stepper motors make them ideal teaching tools. By utilizing the precise control characteristics of stepper motors, they can help students better understand physics and engineering principles.
In summary, stepper motors have the advantages of high precision, controllability, low speed and high torque, and high reliability, but they also have the disadvantages of being easily out of step or out of step, difficult to achieve high rotational speeds, sensitive to load changes, and low efficiency. When selecting stepper motors, it is necessary to consider their advantages and disadvantages as well as the scope of application according to the application requirements to ensure the performance and stability of the system.
Post time: Nov-14-2024
